Fetching Data from a Server using Axios and Promises
In this blog post, we’ll learn how to fetch data from a server in a ReactJS project using Axios and Promises.
What is Axios?
Axios is a JavaScript library used to make HTTP requests. It supports Promises, allowing for easier handling of asynchronous operations. It’s commonly used for interacting with APIs
It’s often used to send asynchronous HTTP requests to REST endpoints.
What is a Promise?
Promises are objects that represent the eventual completion or failure of an asynchronous operation.
Asynchronous operations
are tasks that start and finish at different times, allowing other tasks to run in between. They are used when a task is expected to take a long time to execute, like fetching data from a server.
They can be in one of three states:
- The promise is pending: It means that the final value (one of the following two) is not available yet.
- The promise is fulfilled: It means that the operation has been completed and the final value is available, which generally is a successful operation. This state is sometimes also called resolved.
- The promise is rejected: A failed operation
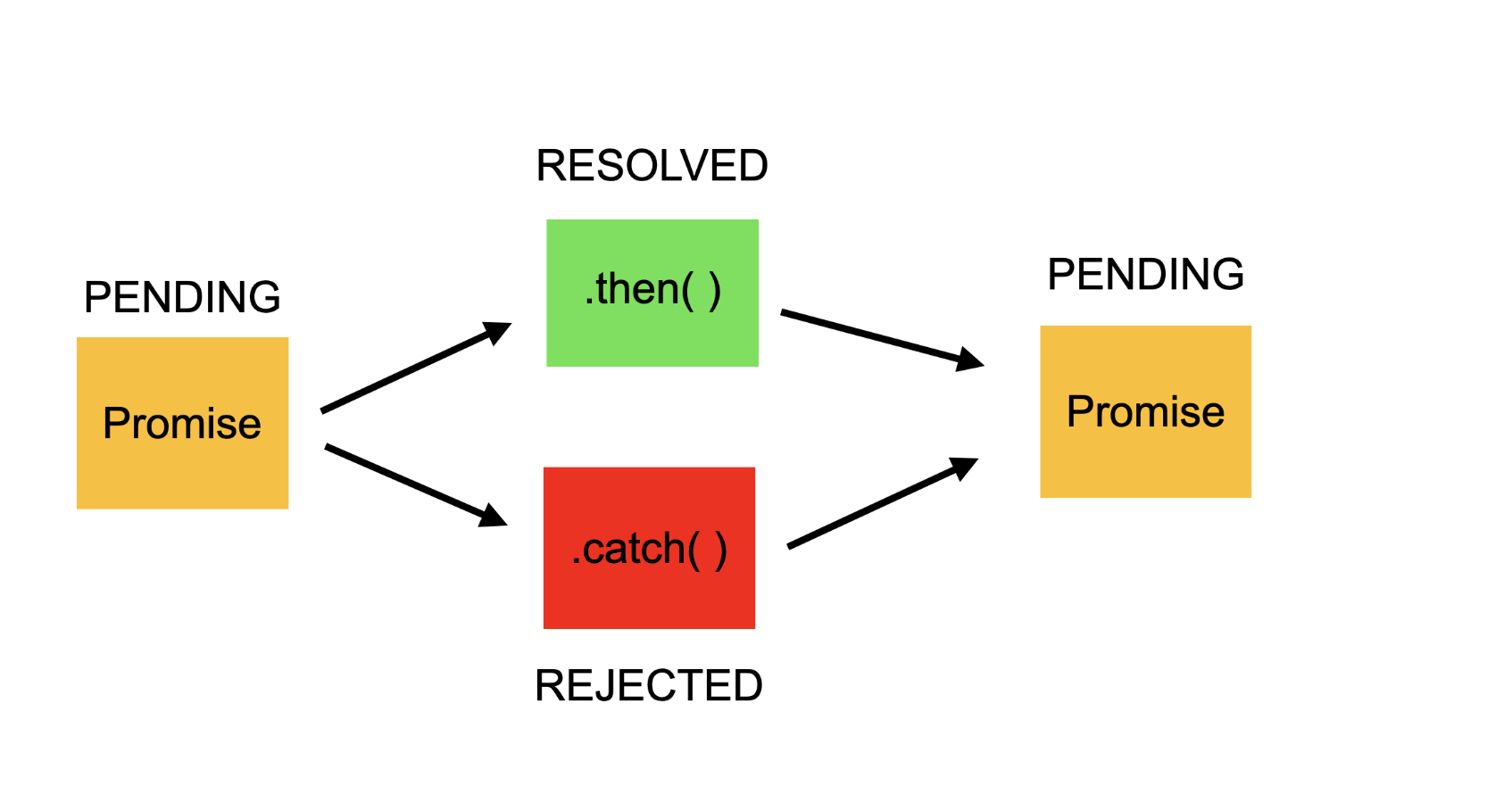
Promises are used to handle callbacks in a more manageable way, avoiding what’s known as “callback hell”.
Steps to Fetch Data
Step 1: Install Axios
First, we need to install Axios. Run the following command:
npm install axios
Step 2: Import Axios in your Component
Next, import Axios in the React component:
import axios from 'axios';
Step 3: Use Axios to Send a GET Request
Now, we can use Axios to send a GET request to a server:
axios
.get(baseUrl)
.then(response => {
const notes = response.data
console.log(notes)
})
use Async/Await
const getAll = async() => {
const response = await axios.get(baseUrl)
return response.data
}
In the above code, axios.get() sends a GET request to the specified URL.
Axios' method get returns a promise that resolves to the response from the server.
it means that the Promise has successfully completed its asynchronous operation, which in this case is getting a response from the server.
The then method is called when the Promise is resolved, and the catch method is called if an error occurs.
Use Axios to Send a Post, Delete, Put Request
const create = async (newObject) => {
const config = {
headers: { Authorization: token },
}
const response = await axios.post(baseUrl, newObject, config)
return response.data
}
const remove = async (id) => {
const config = {
headers: { Authorization: token },
}
const response = await axios.delete(`${baseUrl}/${id}`, config)
return response.data
}
const update = async (newObject) => {
const config = {
headers: { Authorization: token },
}
const response = await axios.put(`${baseUrl}/${newObject.id}`, newObject, config)
return response.data
}
This sends a POST request to the URL specified by baseUrl
newObject is the data you send to the server
config is an object that holds configuration options for the request